EV Generations
First Generation EVs — Built from Gas-Powered Cars
Some electric vehicles are modified versions of gasoline-powered cars. The Hyundai Kona, for instance, is available with either a gasoline powertrain or an electric one.
These EVs may feel more familiar to drivers and may be less expensive to repair because they share many parts in common with a more common electric car.
But they do not gain all the advantages of an EV because engineers have had to shoehorn electric drivetrain parts into spaces built for gasoline-powered cars.
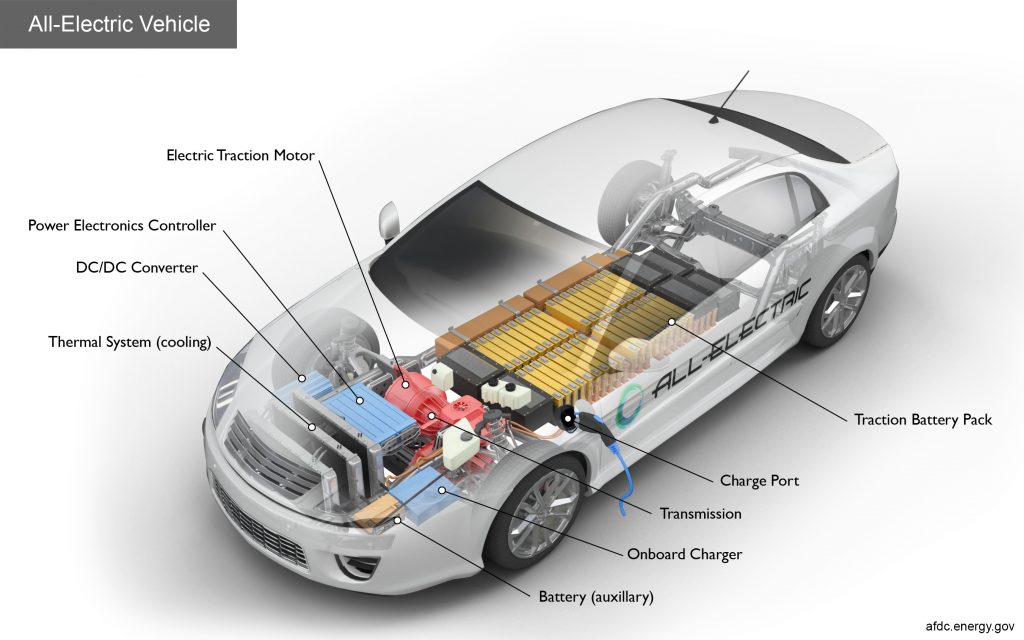
Second Generation EVS — EVs from the Ground Up
Automakers now design most EVs as dedicated electric cars. This allows new design possibilities. For instance, electric cars lack a traditional transmission, so a clean-sheet EV design does not require the traditional transmission hump separating the driver and passenger in a vehicle’s cabin. All an electric vehicle’s moving parts can fit beneath the cabin floor and in the wheel wells.
This allows designers to create uniquely spacious vehicles.
